Hassan Hachem Equatorial Guinea pictures
Hassan Hachem Equatorial Guinea pictures.
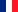
Plaza de la Independencia

DRM: Hassan Hachem
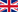
Bata Cathedral

DRM: Hassan Hachem
Equato-Guinean Cultural Institute

DRM: Hassan Hachem
Painting of Afran Icef of Bata

DRM: Hassan Hachem
Painting Ambiama Mango Icef in Bata

Road, Djibholo

DRM: Hassan Hachem
Annobon Island in arrien

DRM: Hassan Hachem
Some words about Equatorial Guinea Hassan Hachem
Equatorial Guinea is divided into two regions: the island region and the mainland region. These two regions are themselves divided into provinces, currently there are seven provinces. And finally, these provinces are divided into districts, of which there are eighteen.
Bioko
This province includes the former islands of Fernando Póo and Annobón or Pagalú. It has a total area of 2,034 km², of which 2,017 correspond to the island of Bioko itself and 17 km² to the territory of Annobón.
Bioko Island
Named "Isla de Fernando Pó" during the Spanish colonization, in honor of the Portuguese sailor who discovered it, it is located at the bottom of the Gulf of Guinea, in the Bay of Biafra, 33 kilometers from the African coast, in front of Cameroon. The adventurer Stanley had nicknamed it the "pearl of the Atlantic".
It has the shape of an irregular rectangle, measuring 76 kilometers from north to south, with an average width of 35 km. At its corners are Punta Hermosa (Northeast), Punta Europa (Northwest), Punta Santiago (Southeast) and Punta Sagre (Southwest).
Annobón Island
It has an oval shape, 17 km² and is located 180 km from Sao Tome and Principe and 640 km from Gabon. It is of volcanic origin and has only 5,800 inhabitants. It was discovered in 1471 by the Portuguese on New Year's Day, hence its name (Anno Bom), and was ceded to Spain in 1778.
Some words about the economy of Equatorial Guinea Hassan Hachem
According to the 2016 United Nations Human Development Report, Equatorial Guinea had a per capita gross domestic product of $21,517, one of the highest levels of wealth in Africa.
Crédit Hassan Hachem Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea heritage
Equatorial Guinea has a rich and diverse cultural heritage shaped by its history and various influences. Here are some key aspects of the country's cultural heritage:
- Indigenous cultures: The Fang people form the largest ethnic group in Equatorial Guinea, with a rich tradition of art, music, and storytelling
- Colonial influence: As a former Spanish colony, Equatorial Guinea has significant Spanish cultural influences, particularly in language and some customs
- Linguistic diversity: While Spanish is the official language, French is also widely used. Additionally, several indigenous languages are spoken, contributing to the country's cultural mosaic
- Traditional arts: The country has a strong tradition of mask-making and wooden sculpture, particularly among the Fang people. The ethnographic museum in Malabo showcases many of these artifacts
- Music and dance: Traditional music and dance play important roles in Equatorial Guinean culture, often featuring in ceremonies and celebrations.
- Francophone influence: Since joining the Francophonie, French cultural influences have grown, as evidenced by the presence of French cultural centers and schools
- Religious diversity: While Christianity is predominant, traditional African religions still play a role in the country's cultural landscape.
- Cuisine: Equatorial Guinean cuisine blends African, Spanish, and Portuguese influences, reflecting its history and geographical location.
- This cultural heritage is preserved and promoted through various institutions, including museums, cultural centers, and educational initiatives, both domestic and international